Google’s Earthquake Alerts Hit 790 Million Warnings — And They’re More Accurate Than You Think
July 21, 2025 | by Admin
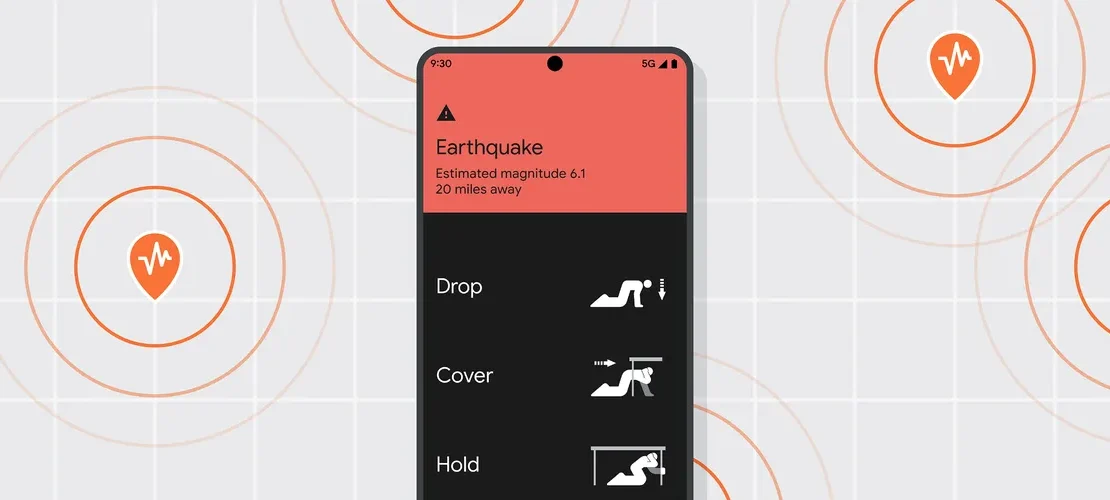
Google’s Android Earthquake Alert system was first developed in 2020. However, the feature was initially available to a limited number of devices and regions. Google had targeted to cover all US states by September 2024. It also rolled out the feature to WearOS-supported smartwatches to ensure that most users are given access to this life-saving feature.
Google’s Android Earthquake Alert Works by Using the Data from the Accelerometer
Ever wondered how Google’s Android Earthquake system works? Well, it relies on the very input from your smartphone. It uses the information from the accelerometer sensor of the Android device, sends it to Google’s server, and analyzes whether other users are facing a similar motion disturbance or not. After analysing location and motion data from multiple users, the system identifies the estimated magnitude and epicentre of the earthquake and sends an early warning to the users.
The alerts are sent in two ways: Take Action Alert and Be Aware Alert. The former alert is issued in case of moderate to extreme shaking, whereas the ‘Be Aware Alert’ is issued in case of weak to light shaking.

Google says that the feature has worked well and saved millions of lives
Google says that nearly 2.5 billion users have access to the advanced Earthquake Alert system of Android. Until now, the system has identified over 2,000 earthquakes and has issued nearly 790 million warnings.
During the Earthquake that hit the Philippines in November 2023, the alert system sent warnings to over 2.5 million users even before they could feel an actual shaking. Similarly, when an earthquake with a magnitude of 5.7 hit Nepal in 2023, the system sent over 10 million alerts. The first alert was issued 15.6 seconds after the earthquake.
Google says that it is continuously working to make the system more reliable. The median absolute error of the first magnitude estimate of the feature stands at 0.25. This makes it even more reliable than traditional seismic networks.
RELATED POSTS
View all

